HIPAA regulations ensure every healthcare provider is accountable for the confidentiality and protection of patient data.
Cardiologists deal with some of the most intimate aspects of a person’s health, from heart conditions to life-saving interventions. Cardiologists have a responsibility to safeguard patient data with the utmost care and diligence.
This blog post will discuss the recent updates to HIPAA regulations and how they affect cardiology practices.
Do the New HIPAA Laws Impact my Cardiology Clinic?
In 2024, significant updates were implemented to strengthen HIPAA’s reach for patient privacy and security. These updates touch on various critical aspects of practice management, including data sharing and cybersecurity.
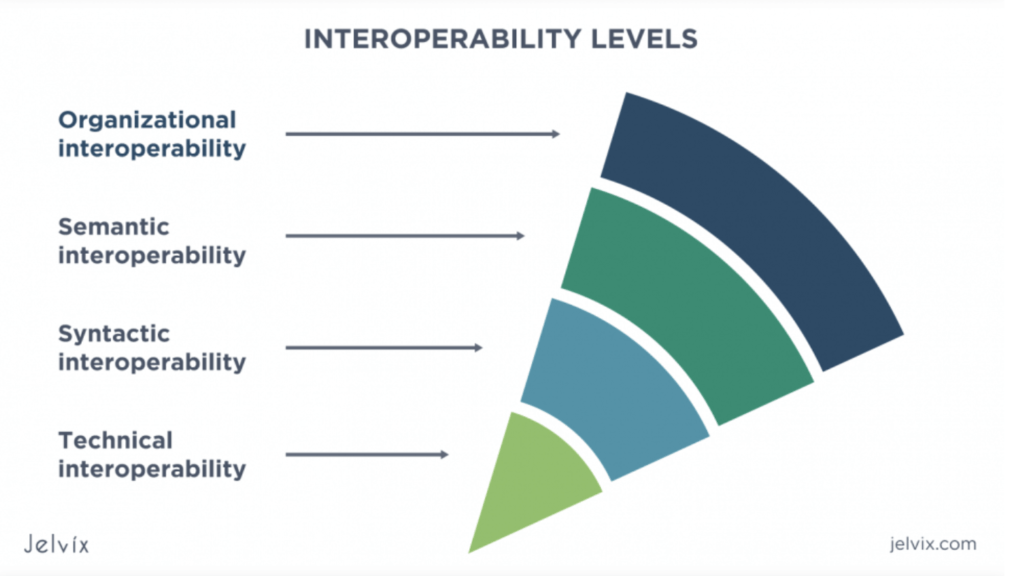
One significant update to HIPAA is the emphasis on interoperability. Interoperability ensures that vital medical information can be securely shared between your clinic and external entities, such as hospitals, laboratories, and primary care physicians. This facilitates comprehensive care coordination, enabling timely interventions and informed decision-making to optimize patient outcomes. Clinics must ensure that their systems can talk to each other effectively while keeping patient data safe.
Another key change to the HIPAA privacy rule involves value-based billing within health information technology. Value-based billing emphasizes patient outcomes instead of just focusing on the number of services provided. It is about delivering quality care that improves patients’ lives.
This shift requires adjustments to practice style and billing processes to align with these new reimbursement models while ensuring the protection of individually identifiable health information and electronic protected health information.
Impact of HIPAA Updates on Cardiology Clinics
Cardiology clinics must adapt to the impact of HIPAA updates given the collaborative role they take on with other healthcare providers. Improving software and information systems, changing operations, and identifying new areas for how to share and encrypt sensitive information will be required. This includes switching to DICOM Structured Reporting and other universally accepted coding standards.
Many aspects of the new HIPAA laws are now being incorporated in EHR software, so for some, making the transition is as easy as following the updates and paying attention. However, for those with outdated or ill-fitting EHR software, then these changes will be cumbersome.
Value-based billing and patient-centered care are now virtually required aspects of maintaining your practice’s HIPAA compliance. By neglecting these changes, your practice would see significant barriers in reimbursement rates. Like every other healthcare practice, cardiology clinics will be evaluated on the effectiveness and efficiency of their interventions, which might require slow productivity or optimizing your operations for better patient outcomes.
To thrive in this value-based model, cardiology clinics must adopt a holistic approach to patient care, focusing on intentional decision-making during the care process, analyzing and improving operations, and providing clear patient education. Businesses should start tracking patient outcomes more closely and implementing evidence-based practices so that clinics can demonstrate their value to patients’ lives while maximizing reimbursement under value-based payment models.
Ultimately, by embracing interoperability and value-based billing, cardiology clinics can position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. Prioritizing collaboration, quality care, and patient-centered practices allows clinics to navigate the challenges posed by HIPAA updates and thrive in delivering exceptional care to their patients.
Challenges of HIPAA Compliance as a Cardiology Clinic
The recent updates to HIPAA regulations have profound implications for cardiology clinics and the broader healthcare landscape. These changes underscore the importance of safeguarding patient privacy and security while adapting to evolving healthcare practices and technologies.
In cardiology settings, key security features in the cardiology information system (CIS) or electronic health record system (EHR), such as user authentication, event logging, redundant off-site archival copies, and a nonvolatile archival system are growing increasingly important.
Maintaining these standards in a cardiologist’s clinic can be challenging. Cardiology clinics that focus on healthcare interopabilities must ensure strong security settings, which can be limited by their budget and technologies. A cardiology EHR system can help secure interoperability features such as enabled data-encoded structured reporting for anonymized information sharing.
The increasing importance of technologies means that even small clinics must account for enterprise-level cybersecurity measures, which can be challenging to do without a robust CIS system. Clinics must rely on cloud-based, secure cardiology EHR to protect patient information from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Overall, the recent updates to HIPAA reflect a proactive approach to addressing challenges in practice outcomes and operational efficiency.
Healthcare organizations who embrace these changes, while challenging, will ensure they are future-proofing their practice for the increasingly digital world.
Steps to Ensure Compliance in Your Cardiology Clinic
In healthcare, compliance is non-negotiable. By understanding the latest HIPAA changes and taking proactive steps to adapt, you can ensure that your cardiology clinic remains on the right side of the law while delivering quality care to your patients.
To do so, start by addressing the following steps:
- Audit your current EHR software and cardiology practice management software to identify the barriers your team regularly encounters. Friction, wasted time, and poorly designed features are not only indications that you should move to new EHR software but that you should be looking for these kinds of features and software that support these features.
- Look for software that focuses on interoperability and value-based care, as these are the two biggest incentives that stem from the HIPAA changes. While interoperability is added to your clinic, it’s important to implement strong security protocols and data encoding for inter-provider communication. You will need to leverage the right health information software to facilitate secure health data exchange and implement robust safeguards to protect electronic medical records and personal information.
- Keep patients informed of changes while they evolve to reduce patient friction and patient care performance.
- Hire consultants or experts to educate on the best practices for the new medical reporting system or incentive programs.
Failure to adhere to HIPAA regulations can result in serious consequences, including potential HIPAA violations and penalties. Therefore, cardiology clinics must remain vigilant and proactive in their efforts to maintain compliance and uphold the trust and confidentiality of their patient’s health information.
By aligning their practices with HIPAA regulations, cardiology clinics can avoid costly violations, enhance patient care delivery, and strengthen relationships with health plans and other healthcare stakeholders.
Invest in a Compliance- and Cardiology-focused EHR Software
With an understanding of what is at stake, how can cardiology practices ensure compliance with these new regulations?
Investing in powerful EHR software is one of the best ways to stay ahead of the new HIPAA changes. Cardiology clinics do not need to spend enterprise budgets on EHR software that will maintain compliance but operate poorly at the clinic level.
GEMMS ONE is a great example of how compliance can be built into user-friendly software. GEMMS ONE is also the only cardiology-focused EHR software, so this means it comes ready-made for successful business outcomes in cardiology clinics.
For example, when it comes to value-based billing, you might need to revamp your billing practices to capture the actual value of the care you provide. This could involve investing in new billing software or training your staff on the intricacies of value-based reimbursement.
Clinics should ensure their systems are compatible with other healthcare providers for interoperability. This might mean upgrading electronic health record (EHR) systems or implementing new protocols for securely sharing patient information.
Staying Compliant and Avoiding Penalties
Navigating these changes can be challenging, but you do not have to do it alone. Resources are available to help you stay on top of HIPAA compliance, avoid HIPAA violations, and ensure your clinic is well-prepared for the future.
GEMMS ONE offers a range of solutions designed to support cardiology clinics in their compliance efforts. From training modules to cybersecurity assessments, we have everything you need to stay ahead of the curve and protect your patients’ sensitive information.
At GEMMS ONE, we are committed to helping cardiology clinics navigate these changes smoothly. With our expertise and resources, you can rest assured that your clinic is in good hands. We are here to support your compliance efforts and keep your practice running smoothly. Contact us today to learn how we can assist you or to schedule a demo.